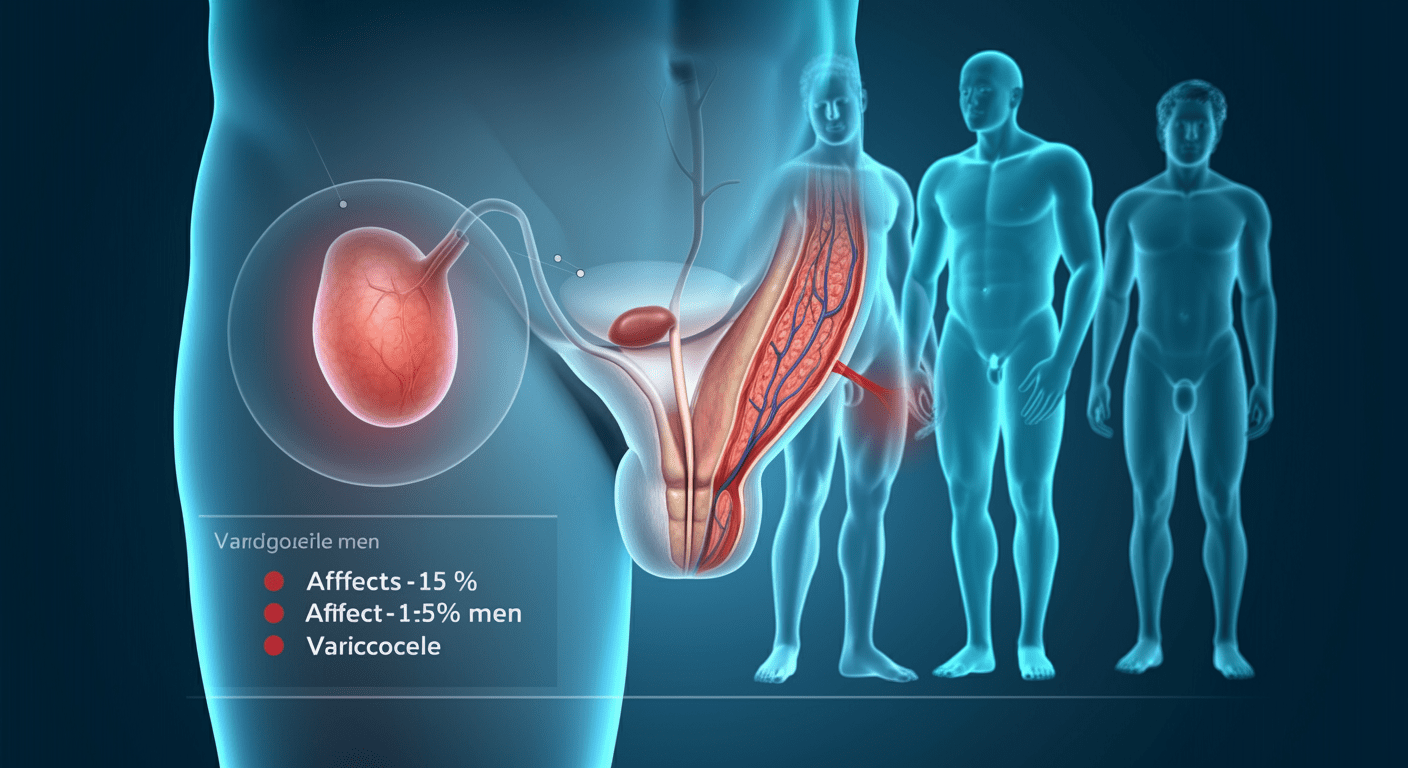
Varicocele is a relatively common condition in men, yet many remain unaware of its existence until they experience symptoms or fertility issues. This article delves into the prevalence, causes, symptoms, impact on male fertility, and treatment options for varicocele. We will also analyze how this condition affects men’s health and what steps can be taken for early detection and management.
Understanding Varicocele
A varicocele is a condition characterized by the enlargement of veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins in the legs. These veins, known as the pampiniform plexus, play a crucial role in regulating the temperature of the testicles, which is essential for healthy sperm production. When these veins become enlarged or dysfunctional, they can lead to increased testicular temperature, potentially affecting sperm quality and fertility.
How Common is Varicocele in Men?
Is varicocele a common condition in men? The answer is yes. Research shows that varicocele affects 15% to 20% of all men, making it a prevalent male reproductive health issue. However, the condition is even more common in men diagnosed with infertility, with a 40% prevalence rate among infertile men.
Varicocele is particularly frequent in young men, typically between the ages of 15 and 25, with the majority of cases occurring on the left side of the scrotum due to anatomical differences in venous drainage.
Causes and Risk Factors of Varicocele
Although the exact cause of varicocele is not fully understood, medical experts believe that it results from malfunctioning valves in the spermatic veins, leading to blood pooling and increased pressure. Several factors contribute to its development:
- Anatomical Factors: The left testicular vein connects to the left renal vein at a right angle, making it more prone to increased pressure and valve failure.
- Genetic Predisposition: Men with a family history of varicose veins or circulatory issues may be at a higher risk.
- Increased Abdominal Pressure: Strenuous physical activity, prolonged standing, or heavy lifting can contribute to varicocele formation.
- Obesity: Excess weight can impact blood circulation and increase pressure on the veins.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Some studies suggest that hormonal imbalances might play a role in varicocele development.
Symptoms of Varicocele
While some men with varicocele experience no symptoms, others may notice:
- Scrotal Pain or Discomfort: A dull, aching pain that worsens after standing for long periods or physical activity.
- Visible Swelling or Enlarged Veins: A “bag of worms” appearance may be noticeable in the scrotum.
- Testicular Atrophy (Shrinkage): The affected testicle may become smaller due to prolonged exposure to excess heat.
- Fertility Issues: Varicocele can impair sperm production and quality, leading to infertility.
- Heaviness in the Scrotum: Some men report a sensation of heaviness or dragging in the testicle.
How Varicocele Affects Fertility
Varicocele is one of the leading reversible causes of male infertility. The condition affects sperm production in several ways:
- Increased Testicular Temperature: Since sperm production requires a lower temperature than body heat, an elevated testicular temperature can hinder sperm development.
- Reduced Sperm Quality: Varicocele can lead to lower sperm count, reduced motility, and abnormal sperm morphology.
- Oxidative Stress: Blood pooling in the veins can result in higher oxidative stress, damaging sperm DNA.
According to studies, 40% of men with primary infertility and up to 80% of men with secondary infertility (previously fathered a child but now experiencing difficulty) have varicocele.
Diagnosis of Varicocele
A varicocele can often be diagnosed during a routine physical examination. Common diagnostic methods include:
1. Physical Examination
A doctor may detect varicocele by palpating the scrotum while the patient is standing. The “Valsalva maneuver,” which involves bearing down while holding one’s breath, can help in identifying smaller varicoceles.
2. Scrotal Ultrasound
If a physical examination is inconclusive, a Doppler ultrasound can confirm the diagnosis by detecting enlarged veins and abnormal blood flow patterns.
3. Semen Analysis
For men experiencing infertility, a semen analysis may be recommended to evaluate sperm count, motility, and morphology.
Treatment Options for Varicocele
Not all cases of varicocele require treatment. However, intervention is often recommended in cases of infertility, persistent pain, or testicular atrophy. The primary treatment options include:
1. Varicocelectomy (Surgical Repair)
Varicocelectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves tying off the affected veins to redirect blood flow through healthier veins. It is performed using one of the following techniques:
- Open Surgery: Traditional approach using a small incision in the groin area.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A less invasive procedure with smaller incisions and faster recovery.
- Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: The most precise technique with the lowest recurrence rate.
2. Embolization (Non-Surgical Treatment)
In embolization, a small catheter is inserted into the vein to block blood flow to the varicocele. This method is less invasive and has a shorter recovery time than surgery.
3. Lifestyle Modifications and Management
For men with mild symptoms, simple lifestyle changes may help alleviate discomfort:
- Wearing supportive underwear to reduce scrotal pain.
- Avoiding heavy lifting to prevent increased abdominal pressure.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to improve circulation.
- Using pain relievers like ibuprofen for mild discomfort.
Can Varicocele Be Prevented?
While varicocele itself may not always be preventable, men can adopt certain habits to reduce their risk and maintain testicular health:
- Avoid prolonged standing or excessive physical strain.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants to combat oxidative stress.
- Exercise regularly to promote healthy blood circulation.
- Stay hydrated to support proper vascular function.
Final Thoughts
So, is varicocele a common condition in men? Absolutely. It affects nearly 1 in 5 men and is a leading cause of male infertility. While many men may never experience symptoms, those who do should seek medical advice to determine the best course of action.
If you are concerned about varicocele, experiencing testicular pain, or facing fertility challenges, consulting a healthcare provider can help you explore treatment options tailored to your needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Varicocele affects 15-20% of men and is more prevalent in those with fertility issues.
- It can impair sperm quality and testicular function due to increased heat and oxidative stress.
- Diagnosis is typically made through physical exams and scrotal ultrasound.
- Treatment includes varicocelectomy surgery, embolization, and lifestyle changes.
- While not always preventable, healthy habits can support testicular health.
By staying informed and proactive, men can take control of their reproductive health and improve their overall well-being. If you suspect you have a varicocele, early diagnosis and management can make a significant difference in your health and fertility outcomes.